A site without a definite structure is as good as building a castle in the air and this defines the significance of an organized site and how essential it is for both users and SEO.
While the user needs this structure to maneuver your site from one page to the other, also note that Google uses the structure of your site to weigh what is important in your content and what is not.
It is now crystal clear that the sole aim of any website is to make ready valuable information in accessible manner. This information in turn is distributed to various internal pages that form a website.
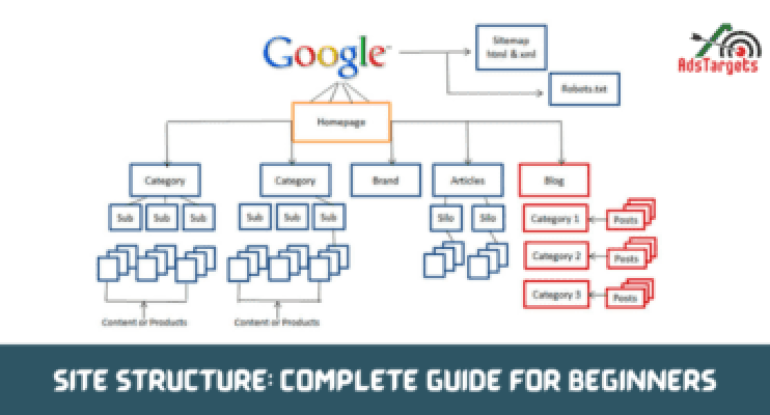
Website structures define the architecture of a site for search engines and users alike.
The structure of a site basically means how all the different pages on a website are connected to each other. This can be accomplished using internal links, which present the hierarchy and organization of your website to the search engine algorithms.
More importantly, site structure is a holistic approach and this has to do with how your content will live, also about navigation, user experience, and the communication of meaning and its significance to the different algorithms and bots that creep your site.
This guide titled: Site Structure: Complete guide for beginners is timely as it hopes to make a case as to why site structure is important to both SEO and users and, as well, on how to set up the site structure and other site structure-related issues of concern.
Table of Contents
Toggle#1. What is site structure?
Whether it’s referred to as site structure, information architecture, or any other synonymous term, it refers to the manner in which information (content of any kind) is organized online.
This includes not just page hierarchies, but internal linking, taxonomies, navigation, metadata, etc. Essentially, site structure is the foundation upon which all of your digital marketing is built and upon which all your ranking efforts rely.
The significance of this can be felt not just from the user’s angle but also from search engine optimization.
#2. Why is site structure important?
Site structure is very important in all ramifications. To me, one of the reasons for having a well-structured site is to offer the best experience to your users. There are cases where site structure may not necessarily have a positive effect on SEO, but don’t forget, for the sake of other users, you MUST place emphasis on it.
Always make your site a place where every visitor who visits should be able to easily find the information or products they are looking for.
While users on their part should also know where they are on your website and how to find what they are searching for. Imagine you are visiting a superstore where hardware is being sold for the first time, and none of the passages were labelled and there is no one around to help you find what you need.
The question now is, would you come back to this hardware store again? Or would you leave and find another competitor that could help you find what you need?
This is where you will discover that structuring your website is instrumental to both its usability and findability. The inability of any sites to be well structured to help guide visitors to the information they’re looking for is detrimental.
Additionally, site structure helps to determine how search engines crawl and index your content, and how the link equity flows throughout your site.
Importance of site structure for users
A well-structured site must impact users, but when it fails to give visitors what they are looking for in terms of information or product, it becomes difficult for becoming customers.
The only way to go from here is for you to help your visitors navigate your site and this can be achievable with a good site structure.
Remember, navigating is easy though, but you need to categorize and link your posts and products so they can be easily found. New visitors should be able to instantly grasp what you’re writing about or selling.
Importance of site structure for SEO
A good site structure largely has a positive effect and stands a chance of being ranked in search engines. For better understanding, there are reasons that account for this:
a. It helps Google ‘understand’ your site
One of the ways Google has a fair understanding of how to find some interesting and valuable content on your site is through a good site structure. This helps search engines to have an in-depth knowledge of your site basically of what you’re selling or you are into.
A magnificent site structure can also help search engines find and index content more easily and quickly. However, a good structure should be able to lead to a higher ranking on Google.

b. It prevents you from competing with yourself
It is very true that, as a blogger, sometimes you may have different blog posts written around the same topic. If your site is designed correctly, it can help you avoid competing web pages and keyword cannibalization.
A good internal linking and taxonomy structure becomes key since all those different blog posts can work for you, instead of against you.
c. Good site structure can get you to site links
Sitelinks on SERP show your website’s important pages. This is great and it places SEO on advantage, and this can improve the click-through rate.
Additionally, it also betters your brand’s reputation and as well helps you rank better on SERPs. Google awards site links to websites with an excellent site structure.
d. Improved crawling
Having a well-designed website structure with good internal linking helps your site in no small measure and not only users but also crawlers that crawl your website by letting them discover important pages.
#3. How to have a good site structure
Having a well-structured site has to do with stages that must be adopted in chronological order and this includes:
Homepage
Your site homepage can best be described as an epic centre where the activities of the whole website is navigated. This must be on the top since it’s very important for every homepage to have links to all the important pages of your website and it serves as a guide to users on the information that they need.
After having the homepage on top, right below the main sections or categories, possibly followed by subcategories. On the ground, you’ll find all the individual posts and pages.
Make no mistakes by trying to link to too many pages from your homepage, to avoid cluttering the homepage. A cluttered homepage doesn’t have any impact on your visitors.
Navigation
An ideal site structure must be able to have a navigation or menu which helps visitors to understand your site structure better using the best approach of short phrases and simple language for the content.
This indeed creates a clear navigation path on your site. Your site-wide navigation, therefore, has two main elements and they include the menu and the breadcrumbs.
The menu
Under the menu, this offers common support for navigation on your website by allowing visitors to use the menu to find things on your website. More importantly, it helps them understand the structure of your website.
It is for this singular reason that the main categories on your site should at all times have a place in the menu on your homepage.
Putting everything in just one menu is damaging, especially when you have a big site with lots of categories. This may clutter your site, thereby giving your main menu a poor look. It would be better if you created a second menu if need be.
On a lighter note, do well by not adding too many links to your menu. Or else be ready to face rejection since they will become less valuable, both for your users and for search engines.
Categories
Categories and subcategories are essential in creating a befitting site structure. Creating categories helps your users and Google to follow every bit of your page content that you write.
Additionally, you can divide the blog posts or products on your site into a number of categories and when these categories are outgrown, then you can divide these categories into subcategories, to clear things up again.
This is one way your pages can help your user and Google to understand every single page you write.
Individual Pages
When individual pages and blogs are carefully organized on your website, it gives the audience access to your website in order to have a glimpse of the content they are searching for.
However, the most effective way to structure information on individual pages is with the use of breadcrumb trails, meta tags, and contextual links.
What then are breadcrumbs?
A breadcrumb is a clickable link that provides your website structure for users and can also assist with the viewing of different posts present on the website. A breadcrumb trail helps greatly in adding navigation to the posts and pages on your website.
The Breadcrumbs toolkit is great, which is why it can offer an improved user experience and SEO of your website.
As a fan of a WordPress site, be prepared to enjoy the services of one of the many breadcrumb plugins that are available.
Tags
The essence of tags is to make the grouping together of related content on your website. Though tags may seem to be similar to the categories present on your website, there is a difference between categories and tags.
Tags are categories that are further divisible into sub-categories. However, tags can’t be subdivided and work only by grouping together similar content.
Try not to create too many tags. If you add a new unique tag to every post or article, you’re not structuring anything. Make sure each tag is used at least twice, and that your tags group articles that genuinely belong together.
It is very true that some WordPress themes display tags with each post, while some don’t. Make sure your tags are available to your visitors somewhere, preferably at the bottom of your article or in the sidebar.
Tags are very useful for both Google and your visitors who may want to read more about the same topic.
Contextual internal linking
Contextual links are said to be internal links within the copy on your pages that refer to other pages within your site.
Site structure is all about grouping and linking the content on your site. When a link is said to be contextual, the page you link to should be relevant for someone reading the current page.
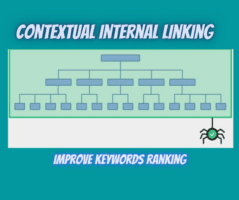
The pages that are seen as the most important and very relevant should be mentioned on several pages across your site, so you’ll link to them from time to time. Even at this, bear it at the back of your mind that, not only is the page you’re linking to relevant, but the context of the link is also very important.
Google, in its wisdom, uses the context of your links in order to establish the needed information about the page you’re linking to using the anchor text or link text. Though, Google looks beyond the anchor text.
In a nutshell, this considers the content around the link to gather extra information while Google is becoming better by the day at spotting related words and concepts.
When links from a meaningful context are added, this allows Google to value and at the same time rank your pages.
Contextual linking for blogs
This is the best way for you to display your writing prowess by being creative. You are duty bound here to write comprehensively on your chosen topics so as to stand a chance to be rated and rank higher.
Writing some main articles that will give you so much recognition has to do with writing different posts about subtopics of the said topic and, most importantly, linking these related posts to your cornerstone articles and from the cornerstone articles back to related posts.
Make sure your blog post writing is comprehensive and your most important pages have both the most links and the relevant links as well.
Contextual linking prospects for online shops
Contextual linking in this context is less known and to avoid being ignored, it is better not to add contextual links to your product descriptions because it could only lead to people clicking away from the page since they only have very few to no pages that are meant to be informed.
Find here some of the significant ways of adding contextual links to your product pages:
- Link from a product bundle page to the individual products
- A ‘related items’ or ‘compare with similar items’ section
- A ‘customers also bought’ section
- A ‘product bundles’ or ‘frequently bought together’ section.
Landing pages
Landing pages are great pages everyone in the digital business would want the audience to find when they search for specific keywords that have been optimized. Take, for instance, people who search for ‘free affiliate marketing training’ should tumble on the page about our free training: affiliate marketing guide for beginners.
This can best be achieved when you approach the content of your most important landing pages with a difference from your previous pages.

For the sake of clarity here, we shall be discussing two types of landing pages: cornerstone pages and product landing pages. Both pages are great in their nature and you’d like people to get on from the search engines.
Though they both require a divergent approach, you must identify what your audiences are looking for is key and this is called search intent. What then is search intent?
Search intent
Search intent form part of the main attributes that are required when you consider setting up your site structure. This is about what you think people are looking for when they enter a query into a search engine.
Have these questions at the back of your mind: What do people want to find and what do they expect to find?
Your ability to think loudly and take actions concerning different possibilities in search intent, believing you really want to cater to different kinds on your site.
Are people just looking for an answer to a question? Are they comparing products before purchase? Or, are they coming with the intent of buying something right away? This is often reflected in the type of query they make.
These and many questions are being pondered on our minds, but when you have an idea of the search intent, it’s essential to make sure your landing page fits the search intent of your audience. Pages can answer more than one search intent, but always have a clear view of most of your important pages.
Cornerstone content pages
No doubt, cornerstone articles are one of the most significant informational articles on your website. This is because it purely focuses on providing the best and most comprehensive information regarding a particular topic.
Cornerstone content is not restricted to blogs but to all different kinds of websites. In simple terms, whichever article reveals everything about a topic you know comprehensively best refers to a cornerstone content article.
Product landing pages
Product landing pages are meant to describe the products so as to attract prospective buyers and, as such, need not be lengthy but focus solely on the buyers.
Product landing pages only need to showcase what your visitors need to know and be convinced. Therefore, you don’t need all the information here.
In as much as you apparently want to rank these pages, that is to say, they need content and not just the content, but the content that is enough for Google to understand what the page is about and what keyword it should rank for.
Whereas cornerstone articles have thousands of words due to their comprehensive nature, a few hundred prove to be enough for product landing pages. The main focus of the content should be on your products.
Maintaining your site structure
Maintaining your site structure is as good as restructuring your content, which is not too bad, especially when you blog a lot, or add other content regularly. It might feel like a task.
Yes, many see it otherwise as not always fun, but trust me, you really have to do it to avoid your site becoming cluttered.
This is one special way to not only fix your site structure but also keep an eye on it while adding new content. It is necessary that site structure should form part of your long-term SEO strategy.
Evaluate your menu
As soon as there is a paradigm shift in your business goal or website changes, your menu also needs to change alongside performance.
By so doing, you ought to start gradually with your new menu, either one or two levels deep, so as to see if it can fit in more of the pages you have created over the years.
It is possible you’ll discover some pages are still valid but are considered irrelevant to your menu.
Be sure of what you are doing and remember to link to them on related pages and in your sitemaps, so that Google and your visitors can still find these pages. The flowchart will also show you any gaps in the site structure.
Rethink your taxonomy
Making sure you have an overview of your categories, subcategories, and products or posts will definitely go down well with you and this will help you to rethink your site’s taxonomy.

See this as a simple spreadsheet with more visual tools which are used here, like LucidChart or MindNode.
Always crosscheck to ensure you are on the right track when dealing with your product categories and subcategories. At some point, do they still provide a logical overview of your product range or your posts and pages?
When you discover a sharp change somewhere down the line, that one category has been far more successful than others, or maybe you write a lot of blog posts on one subject and very few on others.
Take note, if one category grows much larger than others, your site’s pyramid could be thrown off balance. The best thing to do at this point is to split this category into different categories. But always be on the watch. If some product lines end up much smaller than others, you might want to merge them. Don’t forget to redirect the ones you delete.
In the event that your HTML sitemap is built manually, update that sitemap after changing your site structure.
Clean up outdated content
Cleaning up outdated content is essential for your growth. Most outdated articles might need to be updated and republished and this is the only way for them to regain their relevance.
You stand a chance to clean your site nicely, especially the articles that are outdated but no one reads. In this situation, be mindful and never just delete a page or article.
If Google can’t find the page, it gives your user a 404 error page. With this, both the search engine and your visitor will see this error message saying the page doesn’t exist, and that is a bad experience and thus, bad for your SEO.
Always be smart in situations like this. You can properly redirect the URL of the page you’re deleting, so your user (and Google) lands on a different page that is relevant to them. That could even improve your SEO.
Avoid keyword cannibalization
Your website itself is about a specific topic and this is quite broad or rather specific. When adding content, be mindful of keyword cannibalization. Optimizing your articles for keywords that are all too akin, will rather demolish your own chances of ranking on Google.
If you optimize different articles for similar key terms, trust me, you’re doing yourself badly and it is as good as you competing with yourself, and it’ll make both pages rank lower.
You can help yourself better when you research the performance of your content, and possibly merge and redirect some of it. When merging posts, we recommend creating a new draft by cloning one of the original posts.
This gives you the freedom to work on your merged post without making these changes to a live post.
Conclusion
A site structure is a result of precise thinking and organization and is also an essential part of SEO.
This guide reveals to us several reasons why site structure is important. A good site structure helps both your visitors and Google navigate your site while also making it easier to implement changes and preventing competing with your own content.
These tips used in this article serve as a guide to check and improve your site structure and this is one of the ways you’ll stay on top of things when you create something that is user-friendly.