Do you run an online business or are you part of a company that manages several websites?
Then you know that there are also several Marketing Tags that are created by Marketing Tools (Facebook Ads, Analytics, Google Ads, Linkedin Ads, Hotjar, Email Marketing, Marketing Automation etc.).
To implement these Tags you should put them one by one within the pages of the website, surely involving other departments (IT, Development etc.).
This will certainly lead to issues related to release timing, incorrect tag entries, the status of the implemented tags, and so on.

A big problem, in short.
With a Tag Management System, instead, the development department will have to insert a single snippet of code, making life easier for them (letting them wallow in their code) and making you (marketer) more aware of the project.
In this article, then, you will find the complete guide to using Google Tag Manager, a tag management system that will make your working life easier. Let’s get started!
Table of Contents
ToggleIntroduction to Tags: what they are and practical examples
A Tag is any script or tracking element that we want to insert within our site.
It is, therefore, a portion of JavaScript code that is installed in websites or apps for mobile devices, in order to collect and send usage data to third party services.
Third-party services may be Google Analytics, AdWords, Twitter, Facebook, LinkedIn, etc..
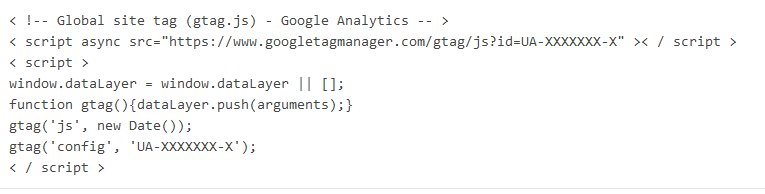
Example Google Analytics tracking tags:
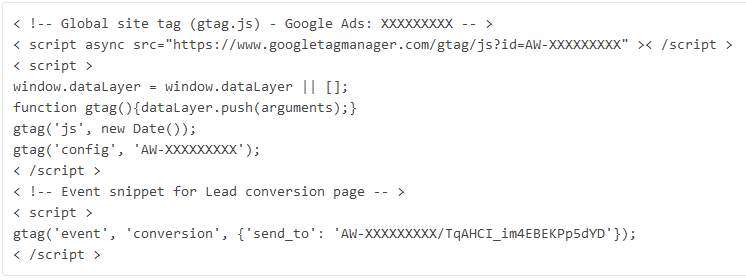
Example Tag Conversions AdWords:
So, as we have just seen, tags are simply fragments of code.
We can add this snippet of code (or tags) directly into our website, copying and pasting it into our template files (such as the header.php file) or we can add the tag indirectly on our website through Google Tag Manager (GTM).
What is Google Tag Manager?
Google Tag Manager (also known as GTM) is the free tag management solution provided by Google.
Through this tool, you can distribute and manage the various tags related to the analysis and monitoring tools on a site or mobile app.
Basically it is a tracking script management platform: it allows you to add a tracking tag without having to physically insert it inside the HTML code of the page.
Google Tag Manager makes the whole coding process much easier.

All you have to do is to install the GTM container code in every page of your site one time and, afterwards, every time you want to insert a tag you can do it directly through the interface of the tool, without having to ask your programmer for support or having to write new code in the site.
In any case, for more information, remember to watch the following video tutorial!
Why should you use Google Tag Manager?
Basically Google Tag Manager is used to save time, code and money. This is because:
- eliminates the need to edit the site code to add, remove or edit tags;
- allows you to test tags very quickly without having to edit the code each time on your site;
- makes multiple monitoring possible even for those who do not have advanced skills.
For example, suppose you want to monitor clicks on all external links on our site, so you can determine the amount of traffic we are sending to other sites (advertisers, affiliates, etc.).
In this case, if we use Google Tag Manager we can complete this task in a few minutes.

Without using GTM we will have to add the event tracking code to each external link, an activity that takes a lot of time and could lead to several errors.
To adapt quickly and economically to changes in Web Marketing, search engines, social media landscape, etc. you need to move quickly.
You cannot afford to take weeks or even months to add a tag to your site just because your developer is too busy updating the product catalogue.
With GTM installed on your site, tags can be added, modified, tested or removed in minutes. This means you can produce and get results faster.
The main advantages of GTM
The first question who starts using this tool is: what is the advantage of adding tags via GTM, when can we add them directly into our site code?
The main advantage is that through GTM, you can easily:
- add;
- remove;
- enable;
- disable;
any tags on your site without having to add code or install additional plugins to your CMS.
Generally speaking, if you don’t use Google Tag Manager you’ll have to manually add or remove tags from one or more template files on your site and you won’t be able to enable or disable them easily: to disable a tag you’ll have to remove it from the template file and, in the same way, to enable another one you’ll have to add it.
In addition, if you want to change the functionality of a tag, you must first manually find the template file in which it was inserted and then modify the code.
In this way, there will be a lot more work to do and more code changes to implement, which could lead to errors especially if the site is large or needs several monitoring tags.
Not using GTM undoubtedly involves a more complex and cumbersome management to keep all tags updated and well functioning on your site.
Such management increases the cost of maintaining your site, involves more work for your developers and, therefore, you end up spending more time and money on tag implementation and management.
That’s why you need to use Google Tag Manager, considering that it is also free and there are no monthly or annual fees, so you really have no reason not to use it.
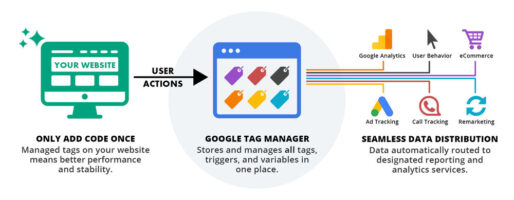
So to sum up, through GTM you can get the following benefits:
#1. More control: in a few steps and a few minutes you can implement Tags and track on your website without having to wait for the programmers’ technical time;
#2. Ease of use: thanks to the intuitive interface of Google Tag Manager you can easily create and edit Tags, Activators and Variables.
It is convenient and practical even for those who are not very familiar with this world;
#3. Practicality: you’ll be able to check if the Tag is working right away, so you can correct any errors promptly without running the risk of losing some analytical data.
All these thanks to the native Preview and Debug system;
#4. Speed: thanks to asynchronous loading, you avoid slowing down the loading of pages;
#5. Cost Savings: by involving fewer resources in code implementation and optimizing timelines, the use of Google Tag Manager also allows you to save costs, as already demonstrated;
#6. Privacy: GTM will also give you a hand in the management of Cookie Law and the dreaded GDPR, making everything much easier and faster.
How to create a GTM account
The first step to start using GTM is to create a free account. If you already have a Google account, creating a Google Tag Manager account is a simple three-step procedure:
=> Go to Tag manager, click on Sign in and log in using your Google account login credentials (email and password);
=> At this point you will need to enter the account name (your company), country and URL of your website;
=> The last step is to indicate the place where you want to use the container (Web, iOS, Android, AMP).
You can select “Web” to install the GTM container on your site, click the “Create” button and finally accept the terms and conditions of service.
FAQ: frequently asked questions about Google Tag Manager
Google Tag Manager makes me independent from the programmer? Yes, but not completely.
Even when you have adequate knowledge of HTML, DOM and JavaScript, you may still need the help of the developer who created your client’s site.
This is because if you are not familiar with the server-side language, the development environment or the database used by your client’s site.
You will need the help of the developer who created it to add server-side code to your data layers or to query the database for your own purposes.
How can I become an expert on Google Tag Manager? To become a GTM expert, you need to develop a very good knowledge of:
– HTML, DOM and JavaScript;
– Google Analytics developer environment;
– Knowledge of DOM Scraping techniques;
– Practical knowledge of regular expressions;
– Knowledge of a server-side language, such as PHP, is a bonus.
Can I distribute the code of the GTM container tag via another tag manager solution? Yes, but this may prevent GTM from working properly. The general rule is not to use more than one tag manager per application.
Are there tags that cannot be distributed with GTM? Yes, GTM cannot be used for the distribution of: synchronous tags, two-part tags and tags that are not compatible with GTM (such as the “Facebook JavaScript SDK”).
You can find a list of all supported tags on the GTM support site.
Does GTM collect data? No, GTM does not collect any data but only passes data to other tools. However, tags activated through this tool may collect data (such as Google Analytics).
What is the difference between GTM and Google Analytics? GTM is a tag manager that is used to distribute and manage various tags. Google Analytics, on the other hand, is a website and app monitoring tool, used to collect, process and generate usage data reports.
Can I use GTM even when I don’t use Google Analytics? Yes. Google Tag Manager is a tag management solution and can also be used to distribute tags not related to Google services.
Conclusions
We have come to the end of this article about Google Tag Manager and all his features.
As you have noticed, it is a tool that has numerous operational benefits and can make your online activity easier and faster. We suggest you to visit the Google support site right now to be guided step by step through the use of this tool.
We hope this article has been useful to you. You are always welcome to visit us at any time!
See you soon!




